Search about search in Google (Alas Googling Google)
BY Eng. Tharindu Weerasinghe
It is not an exaggeration if someone says that, people use “Google” primarily not to search but to make sure that their internet connection is working properly. To that extend, Google has become a very close non tangible online family friend of us. Undoubtedly Google is the most famous search engine around. In this article, you will be given a simple overview of how Google Search works and more importantly some tips to make your search effective and productive.
Google is a highly sophisticated search engine which consists of 4 major parts.
- Crawling the World Wide Web
- Indexing
- Query processing
Let us go into detail, one by one.
- Crawling the World Wide Web
What does it mean? Crawling is a spider act. If further explained, crawling engine (namely, Googlebot) is the spider walk through strands in the web and find every node, the web pages. It is obvious that you need to have some kind of information of sources in-order to provide an answer to a question. So, to give an answer to your query in Google, it should have some sources. Gathering of information is done by web-crawling. It is sophistically handled by Googlebot, which is the Google’s web crawling robot.
Googlebot acts like a web browser; it sends requests to web servers requesting web pages and then after having connected the entire web page is downloaded and handed-over to Google’s indexer. Googlebot is strengthen by high computing power (it has a lot of computers) which allow it to request and receive web pages very quickly than you do on your own. Once it finds other links in one page it tends to keep track of it for later crawling. It can be regarded as crawling after crawling. Anyway, it is called deep-crawling. I think it’s enough about crawling.
- Indexing
Once you have particular information (data) about a page after crawling, then you need to send them for indexing; in-fact that is how Google Works. Googlebot sends the full text of the pages it finds to the Indexer. The indexer stores these pages in Google’s index database. The index is sorted alphabetically by search term with each index entry (search term) storing a list of documents in which the term appears and the location within the text where it occurs. This hierarchy allows quick access to documents that contain user query terms.
To improve search performance, Google ignores (doesn’t index) common words such as the, is, on, or, of, how, why, as well as certain single digits and single letters. These are called Stop Words and they are so common and they hardly narrow a search, so they can be discarded. The indexer also ignores some punctuation and multiple spaces. It converts all letters to lowercase, to improve performance.
- Query processing
Query processing is done by the query processor which mainly has 3 parts.
- Search GUI (Search Box)
- Search Engine
- Result Formatter
Actually how does Google process your search query?
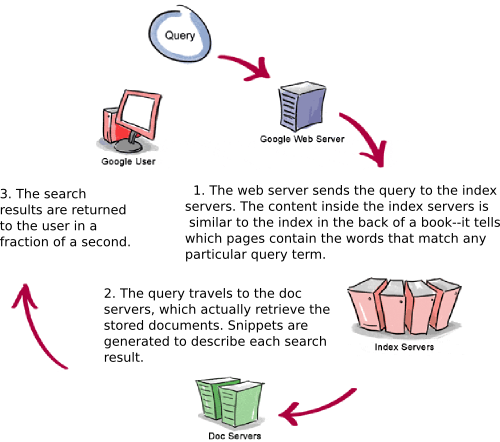
Step1:
You type your search query in the Google’s search box. Then it is sent to the web server and the web server sends the queries to the index servers. Indexers inside the index servers tell us what web pages contain the words that match our search terms.
Step 2:
In the second step, the query travels via the Doc Servers in which we are given the documents that contain our search terms.
Step 3:
After that the final result is formatted by the formatter before presenting them to us.
All these steps are traversed in a fraction of a second.
The following image which describes the query process is obtained from the reference [1] where it is mentioned that the image is a property of Google Inc. Since this image gives you a clear understanding I am using it here. [1]
Some tips to make your search quick and effective:
- As most of the users, you might type the phrase or sentence that you want to search in Google search and examine the results. But if you know some specific search syntaxes then you can search in Google in an effective way.
Advance Search Operators:
- link:
Think that you want to find webpages that have link to a particular web page then you can the keyword link:
Example: If I type link:www.tharinduweerasinghe.com in Google Search Box then Google lists down all the web pages that have links to the site mentioned in the search.
- related:
If you need to list down all the web pages that are similar to the one mentioned in the search box, then you can use the above operator word.
- info:
If you need to retrieve some information that Google has regarding a particular web page then you can use this keyword or the operator word.
- site:
If you use site: syntax in your search query and specify a site that should search your terms then it will list all occurrences of the search term in that particular site.
Example Search: Tharindu Weerasinghe site:pdn.ac.lk
This will list all places that has my name in the Peradeniya University website
- intitle:
This will list the documents containing the search term in the title.
Example Search: intitle: Tharindu Weerasinghe
- inurl:
This will list the documents containing the search term in the URL (web address).
Note: Apart from these operator words you can use + sign to include something and – sign to exclude something from your search. For example, if you type tharindu weerasinghe +cricinfo then it will list the occurrences of my name including the cricinfo web site. And if you type tharindu weerasinghe –cricinfo then it will omit all the results from cricinfo web site.
Hope this article provided you a brief overview of Google Search and some tips to make your search effective.
Reference:
[1] http://www.googleguide.com/google_works.html
 Eng. Tharindu Weerasinghe
Eng. Tharindu Weerasinghe
EMSc | IS, MSc.Eng, BSc.Eng(Hons), CPEng, CEng,
C|EH, SMIEEE, MIEAust, MIET, MACS, MIESL, MCSSL




