|
Construction is one of the most dangerous industries in the world. The ramifications of construction accidents are growing with a trend toward more complex projects .Especially in developing countries, like Sri Lanka. With the construction industry booms and its gross product constantly increases, the number of construction accidents and the deaths have remained stubbornly high. Absolute mortality in the construction industry remains unacceptably high, and those accidents can cause huge losses of life and property, which support the importance of construction safety management. The measurement and assessment of safety performance are therefore urgent and important in order to improve safety management and prevent accidents in all over the world.
Sri Lanka construction companies have a poor degree of risk awareness and do not seems to take health and safety as an important issue. The aim of this research was to understanding of the value of Health and Safety Policy and prevents preventable accidents and illness by ensuring a good reporting system by data and analyzing mechanism of injuries. According to the Dept. of Labour in Sri Lanka 500,000 man days are lost annually due to occupational health hazards. There is a limited list of modifiable occupational diseases in Sri Lanka under the Factories Ordinance No.45 of 1942 as amended by Acts No. 54 of 1961 & No. 12 of 1976. Most of the occupational hazards are not reported as individuals take treatment on their own.
 |
|
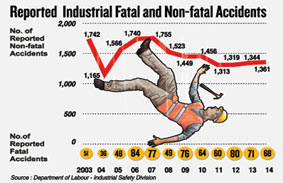
A survey done in the Accident and Orthopaedic Service of the National Hospital in Sri Lanka in year 2015 treated 102321 accidents victims. It has shows 12% of the injuries are due to occupational health hazards. Out of the fatal accidents, 50% are from construction industry. Most of these hazards and accidents are preventable.In this context, as the “legislative protection” is limited to workers in “Factories”, the need to cover all workers beyond “factories” has to be recognized and implemented. |
At present, the Ministry of Labour in Sri Lanka, which is the primary agency for the provision of occupational health & safety services, lacks the institutional capacity to address these issues on its own, while the Ministry of Health has to bear the burden of morbidity and mortality due to occupational hazards It is the need of the hour to recognize the importance of inter-sectorial collaboration to address these issues by developing a national plan of action, strengthen institutional mechanisms and analytical facilities to remedy the situation But the National Policy on Health Information Ministry of Health, Nutrition and Indigenous Medicine is not clear about the occupational health and safety issues.
| My research revealed that many micro, small, medium sized construction companies are unaware of safety policies and do not have safety officials. I had selected 22 construction companies randomly in different levels, to get the reality of the culture of construction. The received responses were comprised of 13.60% and 40.90%% from micro and small construction companies respectively.On the other hand, the responses from medium and large companies were 22.27% and 18.18% respectively. |
|
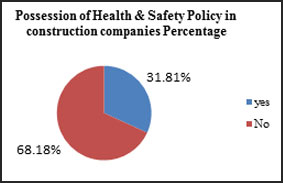 |
The possession of health and safety policy is a legal requirement. It is ensured that the health and safety of organization’s employees and other people affected by organization’s activities. The question intended to explore the existence of health and safety policy in construction companies and determine the general content of existing policies in these organizations. 68.18 % of the companies participated in the questionnaire indicated they did not have a written health and safety policy while only 31.81% reported having a health and a safety policy.
In order to reduce the number and severity of work zone Accident and illness, it is important to know the size and scope of the problem. This can be determined through the collection and analysis of work zone safety-related data with the collaboration of Ministry of Labour and the Ministry of Health .There are also no clearly defined regional, institutional or programme based focal points for health information management in all areas. Notably, some disciplines have developed information systems to cater to their needs, although, there are no proper mechanisms for integration with the national HIS.
Moreover, the lack of integration has led to the repeated capture of the same data elements from different groups, posing an undue burden on the data collection process. Most data collection forms have not undergone timely revisions. But as we inquire we found that there is no proper way of collecting data in the work zones in Sri Lanka. Therefore should introduce or establish a Institution or Ministry to collect data of accidents occurs in all the companies of construction sites to reduce this burden and also should empower and regular to update health and policy in Sri Lanka. It is questioned that all the companies know this policy. Therefore, it should improve health and safety standards at construction.
The Safety of constriction workers in Sri Lanka is woefully neglected area. Many construction workers and owners of construction sites are unaware of the needy of deploying Health and Safety official at the work-sites and even if they had such officers these officers were not aware of safety protocols. Authority and the officials should understand the needs of the hour was a policy that includes strong risk assessment ,management and proper auditing. Everything regarding the safety and Health condition of workers should be listed and checked. Safety Rules, Reporting of injuries & illness, Notifications, Enforcement of Safety Policy, First Aid should be included in the list. And also Government should set up an independent state body to record incidents, including accidents .In construction sites. This body should also look into ways averting such accidents in the future after finding out how they took place. Sri Lanka currently had safety policies that are more suites for developed countries we lacked the resources to implement them. Sri Lanka should have a safety policy more suited to the country and it should be enforced strictly.
During my research I found that although more attention given to the accidents that take place and the resultant injuries sustained by the workers, the general fitness and health of the workers were neglected areas. I would claim, although come up with a proposal on the safety of workers based on my research the government had not yet used it to formulate a practical and workable policy.
Benefits of a Zero Incident Safety Policy
- Safety standards are communicated to all employees.
- Responsibilities for implementing standards are understood and accepted
- Records will document how standards and Best Management Practices are met.
- Internal management control • Cost Avoidance • Improved Quality
- Better Productivity
- Team Building
- Unsafe behavior stands out
- Unsafe behavior is Unacceptable
- Safe Work is influenced through peer pressure
- Consistent planning and task execution
Let's join hands tied Management/Leadership/Employee Involvement
- Employer and employee involvement and communication on workplace-safety and health issues are essential.
- Involve all employees in policy making on safety and health issues.
- Everyone must take an active part in Safety Activities.
If safety goals are not set at zero, an employer sends a message to employees that severe and disabling incidents are acceptable.
- One must understand that the safety culture must be viewed similar to a quality program.
The zero incidents concept must be agreed upon and understood by management first.
We must adopt a safety culture that fits the needs of the organization
[References have been made to the information of the Department of Labour and Ministry of Health and Indigenous Medicine Sri Lanka in formulating some sections of the article]
|